# 面试模版part2
# 目录
[TOC]
# LRU题解的模版✅
- 1、用STL的list双向链表,精简代码
- 2、反思了一下,以前为什么C++设计的时候,迭代器有了end还要rbegin
- 3、这类设计数据结构的方式让我们思考C语言的严版的设计方式和我们C++面向对象的设计方式的异同
- C++设计数据结构,感觉就是推广了C语言数据结构的设计方式,思维方式就很想this指针如何用C语言实现一样
- 4、哈希的时候,那个key或者val,你可以展开思路!比如到迭代器!数组!数组套迭代器啥的!
//要使用unorder_map,它底层是散列,只会映射而不用排序,能够实现$O(1)$
//体现了STL中为什么,有end还要有rbegin的原因
//因为end指向的是指向最后一个元素的下一个节点,而rebgin体现的却是倒数第一个元素的位置
# 2.AC代码
# get借助put精简代码的版本」迭代器的转换
# ✅记忆
std::next(it).base(); //反向迭代器转换为正向迭代器!
1
class LRUCache {
private:
list< pair<int,int> > m_list; //key. val 不能仅val,因为我put的时候要删掉key的map
map<int, list< pair<int,int> >::iterator > m_mp; //key->iterator
int m_capacity;
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) :m_capacity(capacity){
}
int get(int key) {
if( m_mp.find(key) != m_mp.end() ){
int t_key=key, t_val= m_mp[key]->second ;
put( t_key, t_val ); //重新放进去,借助put精简代码
return t_val;
}
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
//如果存在原本的key,管你一样还是不一样
if( m_mp.find(key) != m_mp.end() ){
m_list.erase( m_mp[key] ); //清除list
m_mp.erase( m_mp.find(key) ); //清除map
}
//如果不存在、转换成的不存在
//去除「最久没访问的」
if( m_list.size()==m_capacity ){
//不是front是begin
list< pair<int,int> >::iterator it= m_list.begin();
m_mp.erase( m_mp.find( it->first ) );
m_list.pop_front();
}
//小的
//「坑点!反向迭代器和正向迭代器的转换!」
//std::next(it) 返回指向反向迭代器的下一个元素的迭代器,再通过 std::next(it).base() 将其转换为正向迭代器。
//注意,it 必须是 auto 类型,因为它的类型是一个反向迭代器,无法直接转换为正向迭代器
m_list.push_back( make_pair(key,value) );
auto it = m_list.rbegin();
//发现下面的转换结果是一样的
//cout<<"tempkey="<<it->first<<" val="<<it->second<<endl;
//cout<<"key="<<std::next(it).base()->first<<" val="<<std::next(it).base()->second<<endl;
m_mp[key]=std::next(it).base();
}
};
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
- 上面的,可以不使用迭代器转换,但是会超时22/22
auto it = m_list.begin();
int loop=m_list.size()-1;
//超时原因在这,但是没办法!因为it+=loop不行!it=it+loop也不行!
while( loop-- ){
it++;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
# ✅最终改善后的代码!我们把最久的放在list的末尾而不是首位-避免迭代器转换
class LRUCache {
private:
list< pair<int,int> > m_list; //key. val 不能仅val,因为我put的时候要删掉key的map
map<int, list< pair<int,int> >::iterator > m_mp; //key->iterator
int m_capacity;
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) :m_capacity(capacity){
}
int get(int key) {
if( m_mp.find(key) != m_mp.end() ){
int t_key=key, t_val= m_mp[key]->second ;
put( t_key, t_val ); //重新放进去
return t_val;
}
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
//如果存在
if( m_mp.find(key) != m_mp.end() ){
m_list.erase( m_mp[key] ); //清除list
m_mp.erase( m_mp.find(key) ); //清除map
}
//如果不存在+转换成的不存在
//比较大了
if( m_list.size()==m_capacity ){
//这里改了方向
auto it= m_list.rbegin(); //反向迭代器,但是这里没事!因为我后续只需要获得对应的元素
m_mp.erase( m_mp.find( it->first ) );
m_list.pop_back();
}
m_list.push_front( make_pair(key,value) );
auto it = m_list.begin(); //正向迭代器!
m_mp[key]=it;
}
};
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# 3.面试问:正向迭代器和反向迭代器的区别
正向迭代器和反向迭代器都是用于迭代容器中元素的工具,但它们的方向不同。
正向迭代器是一种顺序遍历容器元素的迭代器,它按照容器中元素的顺序逐个迭代。例如,在一个列表中,正向迭代器将按照列表从左到右的顺序逐个迭代列表元素。
反向迭代器是一种逆序遍历容器元素的迭代器,它按照容器中元素的相反顺序逐个迭代。例如,在一个列表中,反向迭代器将按照列表从右到左的顺序逐个迭代列表元素。
在C++中,可以使用begin()和end()函数获取正向迭代器,使用rbegin()和rend()函数获取反向迭代器。
# Trie-前缀树✅
前缀树,又称字典树,是 N 叉树的特殊形式。
Trie [traɪ] 读音和 try 相同,它的另一些名字有:字典树,前缀树,单词查找树等。
# 字典树类代码
class Trie
{
private:
//标记是否是单词结束
bool isEnd;
Trie* next[26];
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Trie()
{
isEnd = false;
memset(next, 0, sizeof(next));
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
void insert(string word)
{
Trie* node = this;
for (char c : word)
{
if (node->next[c-'a'] == NULL)
{
node->next[c-'a'] = new Trie();
}
node = node->next[c-'a'];
}
node->isEnd = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search(string word)
{
Trie* node = this;
for (char c : word)
{
node = node->next[c - 'a'];
if (node == NULL)
{
return false;
}
}
//借助isEnd来看是不是最终的节点
return node->isEnd;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
bool startsWith(string prefix)
{
Trie* node = this;
for (char c : prefix)
{
node = node->next[c-'a'];
if (node == NULL) {
return false;
}
}
//比如,apple的前缀可以是app,apple
return true;
}
};
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie* obj = new Trie();
* obj->insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj->search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix);
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
# k个1组反转链表
- 个人模版:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/ (opens new window)
- 解体核心:
- 要有哨兵
- 要注意翻转后的位置
- 要注意k个一组,循环的时候是循环k-1次
- 解体核心:
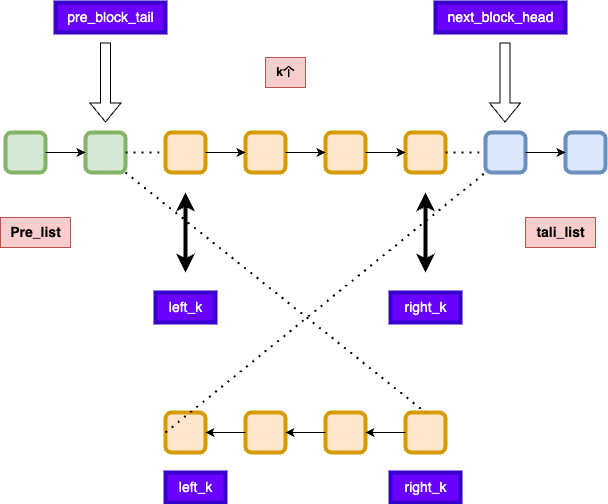
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse( ListNode *head ){
ListNode * sentry=nullptr;
while( nullptr!=head ){
ListNode *temp=head->next;
head->next=sentry;
sentry=head;
head=temp;
}
return sentry;
}
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode* dummy=new ListNode( INT_MAX );
ListNode* preblock_tail=dummy;
ListNode* left_k=head;
ListNode* right_k=head; //初始位置
ListNode* nextblock_head=head; //暂时未知
//如果更新后的,后半部分链表不为空,我们尝试一下
while( nullptr!=nextblock_head ){
//move right, k-1
for(int i=1; i<k && nullptr!=right_k; ++i){
right_k=right_k->next;
}
//说明right和right不足k-1的距离,也就是【left,right】不足k个
if( nullptr==right_k ){
break;
}
nextblock_head=right_k->next;
right_k->next=nullptr; //截断和nextblock的连接
reverse( left_k );
preblock_tail->next=right_k;
left_k->next=nextblock_head;
//update data
preblock_tail=left_k;
left_k=nextblock_head;
right_k=nextblock_head;
}
ListNode* ret=dummy->next;
delete dummy;
return ret;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63